| |
- Polymeric micellar nanotechnology
|
| |
|
|
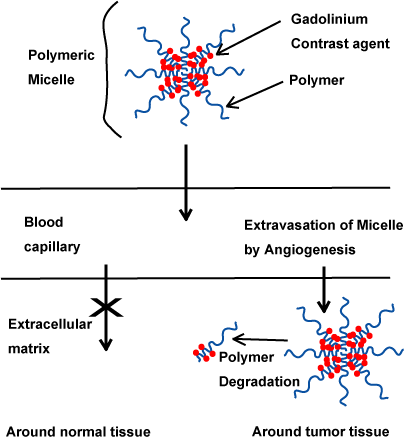
Our one nanotechnology is a polymeric micellar contract agent for magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) diagnosis encapsulated gadolinium-based contract
agent within block copolymer nanoparticle.
The nanotechnology was discovered and formulated by Associate Professor
Yokoyama of Medical Engineering Laboratory Research Center for Medical
Science, Jikei University School of Medicine.
An advantage of this diagnostic agent is to selectively accumulate into
tissue around cancer, since the nanoscale material selectively permeates
into capillary around cancer tissue.
Because of passive targeting having no special selectivity against cell, the contrast after injection would be kept around various cancer tissues within body including primary and metastatic cancer. Moreover, this MRI diagnostic agent is expected to become benefitable diagnositic agent by having both the selectivity against cancer and the accumulation of contrast agent into cancer tissues. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
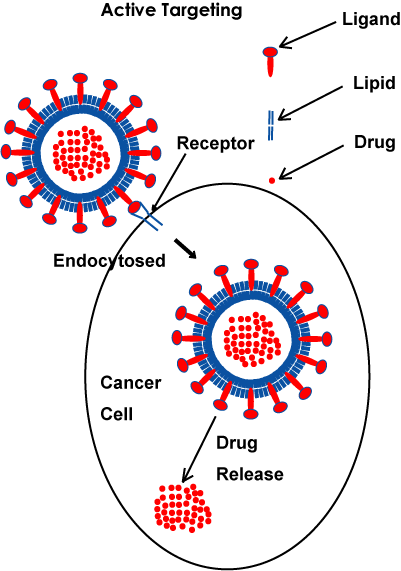
Our one nanotechnology is an active targeting nanotechnology against cancer
by liposome nanotechnology.
The active targeting nanomedicine by the nanotechnology was discovered
and formulated by Professor Maitani of Institute of Medicinal Chemistry,
Fine Drug Targeting Research Laboratory, Hoshi University.
The advantages of this active targeting nanomedicine are to selectively
accumulate into tissue around cancer, since the nanoscale liposome selectively
permeate into capillary around cancer tissue. Moreover, the liposome nanoparticle
is endocytosed into a cancer cell through the selective interaction with
cancer cells. Since a certain membrane receptor in cancer cell have a different
receptor in normal cell, anticancer drugs are encapsulated into liposome
nanoparticles attached with certain ligands targeting against membrane
receptor of cancer cell on the outside of liposome particle. The type of
membrane receptor or the affinity between receptor and ligand differs among
cancer cells.
We formulate an optimal targeting nanomedicine against the type of targeted cancer cell, selecting ligands and active ingredients such as chemicals, biologics or small interfering RNA (siRNA) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|